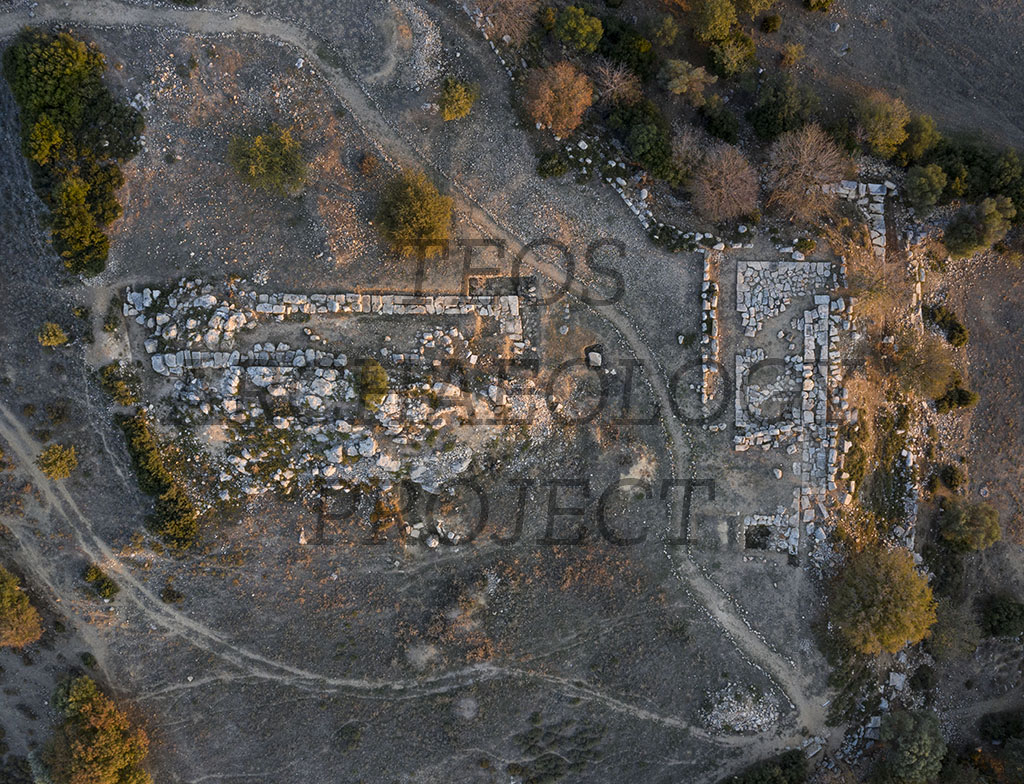

Aerial Photograph of the Acropolis of Teos, Hekatompedos and altar (Kadıoğlu, 2021, 136, Figure 49a)
The Acropolis of the ancient city’s was located on a rocky hill, now called Kocakır Tepe, dominating the North and South Harbours. Today, traces of the structure called the Hekatompedon can be seen on the Acropolis, as well as a possible altar to the east of it, and the terrace wall confining the Acropolis to the east. No architectural terracotta or marble fragments that might belong to the building was found during these investigations. If the flattened rock area to the south is considered to be the stylobate level of the so-called Hekatompedon, and if the bedrock inside the cella was not preserved for cult purposes, then it appears that the temple was raised on a podium c. 2.5 m high.
While the trenches did not return any data about the foundation of the building, a large amount of Late Hellenistic–Early Roman pottery and glass fragments, metal and bone objects, animal bones, terracotta weights, roof tiles, brick fragments, and a leaf-shaped piece of gold jewellery were found. These finds suggest that the area possibly contained a bothros (pit) that was used beyond the Archaic Period.
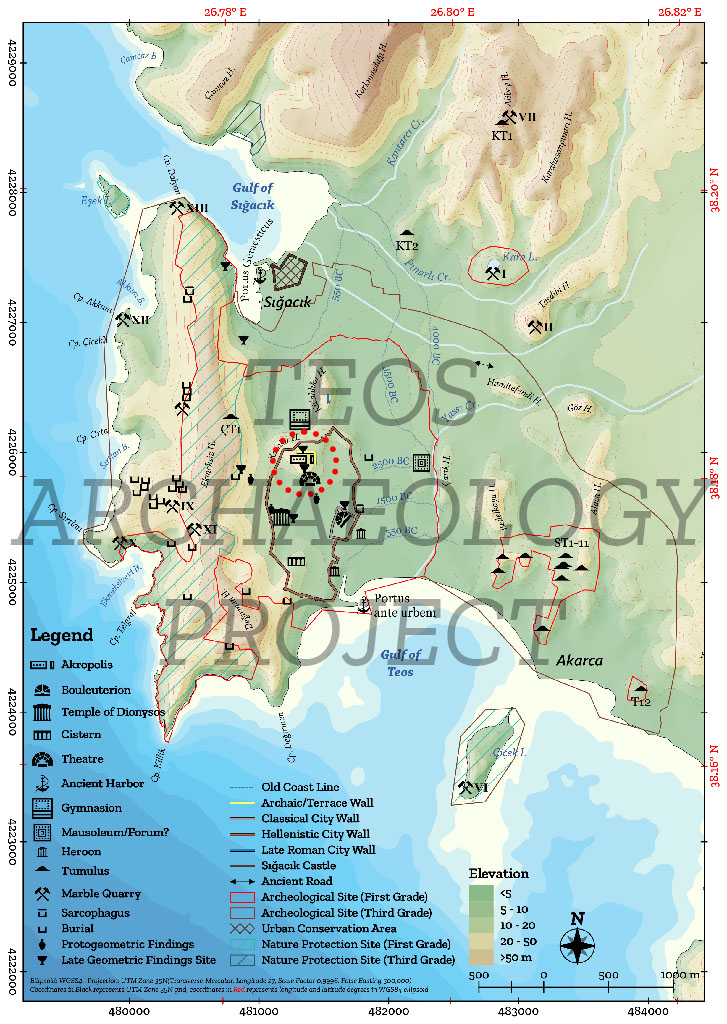
Archaeological map of Teos and its surroundings (Kadıoğlu, 2021, 25, Map 4)
